- Home >
- 研究成果
研究成果
April 25, 2025
A Bayesian Exploration on the Motivational and Behavioral Impacts of Chatbots in Language Learning
May Kristine Jonson Carlon, Julian Rodney Matthews, Yasuo Kuniyoshi, "A Bayesian Exploration on the Motivational and Behavioral Impacts of Chatbots in Language Learning", CHI EA '25: Proceedings of the Extended Abstracts of the CHI, 39, Pages1-7.Abstract
This study investigates the motivational and behavioral effects of chatbot interfaces on knowledge tasks in language learning, focusing on English as a Second Language (ESL) learners. As chatbots gain prominence in education, understanding how user factors—metacognitive awareness, help-seeking behavior, and technology acceptance—interact with interface design is critical for optimizing engagement and performance. We conducted an experimental study comparing conversational and informational chatbots during audio-based learning tasks. Bayesian analysis revealed that chatbot type minimally influenced perceived usefulness, with informational chatbots showing slightly higher engagement. Metacognitive awareness strongly predicted help-seeking tendencies, which positively impacted technology acceptance. These findings offer actionable insights for designing AI systems that enhance user engagement and learning outcomes while balancing reliance on automation. Our work contributes to understanding human-AI interaction in educational technology, emphasizing user-centered design’s role in fostering equitable and effective learning experiences.
April 11, 2025
Self-organized institutions in evolutionary dynamical-systems games
Kenji Itao and Kunihiko Kaneko, "Self-organized institutions in evolutionary dynamical-systems games", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences(PNAS), 122 (15) e2500960122.Abstract
Sustainable resource management requires individuals to cooperate by using common resources within appropriate limits. To achieve this, communities need norms that define which actions are cooperative and which are defective, as well as mechanisms to punish those who violate these norms?together, these constitute “institutions.” How then these norms are organized? While field studies have documented numerous cases of institutions arising spontaneously at the grassroots level, the precise mechanism behind their formation has remained a puzzle. In response to this challenge, we propose a new theoretical framework called the evolutionary dynamical-systems game, which integrates game theory with a dynamical-systems perspective. Specifically, we model resource levels as changing over time in response to players’ actions, and we define each player’s strategy as a “decision-making function” that determines players’ actions depending on resource and players’ conditions. As a result of the evolution of these decision-making functions, we find that players spontaneously establish norms to distinguish cooperative from defective actions and punish those who violate these norms. This demonstrates how institutions can emerge bottom-up, without relying on top-down regulations.
September 20, 2024
Humans flexibly integrate social information despite interindividual differences in reward
Alexandra Witt, Wataru Toyokawa, Kevin N. Lala, Wolfgang Gaissmaier and Charley M. Wu, "Humans flexibly integrate social information despite interindividual differences in reward", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences(PNAS) 121 (39) e2404928121.Abstract
There has been much progress in understanding human social learning, including recent studies integrating social information into the reinforcement learning framework. Yet previous studies often assume identical payoffs between observer and demonstrator, overlooking the diversity of social information in real-world interactions. We address this gap by introducing a socially correlated bandit task that accommodates payoff differences among participants, allowing for the study of social learning under more realistic conditions. Our Social Generalization (SG) model, tested through evolutionary simulations and two online experiments, outperforms existing models by incorporating social information into the generalization process, but treating it as noisier than individual observations. Our findings suggest that human social learning is more flexible than previously believed, with the SG model indicating a potential resource-rational trade-off where social learning partially replaces individual exploration. This research highlights the flexibility of humans’ social learning, allowing us to integrate social information from others with different preferences, skills, or goals.
September 3, 2024
Emergence of economic and social disparities through competitive gift-giving
Kenji Itao and Kunihiko Kaneko, “Emergence of economic and social disparities through competitive gift-giving”, PLOS Complex Systems 1.1 (2024).Abstract
Several tiers of social organization with varying economic and social disparities have been observed. However, a quantitative characterization of the types and the causal mechanisms for the transitions have hardly been explained. While anthropologists have emphasized that gift exchange, rather than market exchange, prevails in traditional societies and shapes social relations, few mathematical studies have explored its consequences for social organizations. In this study, we present a simple model of competitive gift-giving that describes how gifts bring goods to the recipient and honor to the donor, and simulate social change. Numerical simulations and an analysis of the corresponding mean-field theory demonstrate the transitions between the following four phases with different distribution shapes of wealth and social reputation: the band, without economic or social disparities; the tribe, with economic but without social disparities; the chiefdom, with both; and the kingdom, with economic disparity and weak social disparity except for an outlier, namely, the “monarch”. The emergence of strong disparities is characterized by power law distributions and is attributed to the “rich get richer” process. In contrast, the absence of such a process leads to exponential distributions due to random fluctuations. The phases depend on the parameters characterizing the frequency and scale of gift interactions. Our findings provide quantitative criteria for classifying social organizations based on economic and social disparities, consistent with both anthropological theory and empirical observations. Thus, we propose empirically measurable explanatory variables and characteristic indices for the evolution of social organizations. The constructive model, guided by social scientific theory, can provide the basic mechanistic explanation of social evolution and integrate theories of the social sciences.
August 7, 2024
Formation of human kinship structures depending on population size and cultural mutation rate
Kenji Itao and Kunihiko Kaneko, "Formation of human kinship structures depending on population size and cultural mutation rate", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 121.33 (2024).Abstract
How does social complexity depend on population size and cultural transmission? Kinship structures in traditional societies provide a fundamental illustration, where cultural rules between clans determine people’s marriage possibilities. Here, we propose a simple model of kinship interactions that considers kin and in-law cooperation and sexual rivalry. In this model, multiple societies compete. Societies consist of multiple families with different cultural traits and mating preferences. These values determine interactions and hence the growth rate of families and are transmitted to offspring with mutations. Through a multilevel evolutionary simulation, family traits and preferences are grouped into multiple clans with interclan mating preferences. It illustrates the emergence of kinship structures as the spontaneous formation of interdependent cultural associations. Emergent kinship structures are characterized by the cycle length of marriage exchange and the number of cycles in society. We numerically and analytically clarify their parameter dependence. The relative importance of cooperation versus rivalry determines whether attraction or repulsion exists between families. Different structures evolve as locally stable attractors. The probabilities of formation and collapse of complex structures depend on the number of families and the mutation rate, showing characteristic scaling relationships. It is now possible to explore macroscopic kinship structures based on microscopic interactions, together with their environmental dependence and the historical causality of their evolution. We propose the basic causal mechanism of the formation of typical human social structures by referring to ethnographic observations and concepts from statistical physics and multilevel evolution. Such interdisciplinary collaboration will unveil universal features in human societies.
August 23, 2023
The Association Between Different Digital Use and Young Adults' Well-being
Yijun Chen, Xiaochu Zhang, Rei AkaishiAbstract
Digital technology, particularly smartphones, has become an integral part of modern life, raising concerns about its impact on well-being, especially among young people. Previous studies have yielded inconsistent results, possibly due to a lack of differentiation between different types of digital use and an overemphasis on the connection between smartphone use and well-being while neglecting confounding variables such as face-to-face communication time. In this pre-registered study, we employed the experience sampling method (ESM) to track the daily activities of 418 individuals over 21 days and analyzed the data using multilevel models and psychometric network models. Our study specifically examined the effects of different communication targets (one-to-one vs. one-to-many) and communication modes (online vs. offline). The findings revealed that digital use has only a small direct effect on well-being, with negative impact of one-to-many online communication (e.g., viewing Twitter or Instagram). Increased digital use was found to reduce offline communication time, indirectly influencing well-being to a large degree. Overall, this study has the potential to reconcile the inconsistent findings regarding the effects of digital technology on well-being with indirect effects through reduction of offline communication time. The negative impact of one-to-many online communication, which constitutes a significant portion of digital use time, warrants further attention.September 27, 2022
Perceptions of social rigidity predict loneliness across the Japanese population
Ryan P. Badman, Robert Nordstrom, Michiko Ueda & Rei AkaishiAbstract
Loneliness is associated with mental and physical health problems and elevated suicide risk, and is increasingly widespread in modern societies. However, identifying the primary factors underlying loneliness remains a major public health challenge. Historically, loneliness was thought to result from a lack of high-quality social connections, but broader cultural factors (e.g. social norms) are increasingly recognized to also influence loneliness. Here, we used a large-scale survey (N = 4977) to assess to what degree the loneliness epidemic in Japan is associated with traditional measures of social isolation (number of close friends), cultural factors (perceptions of social rigidity, as measured by relational mobility), and socioeconomic factors (e.g. income). We confirmed that a lack of close friends is a dominant factor underlying loneliness in Japan. We also found that perceptions of the social rigidity in one’s environment was a major correlate of loneliness. Subjects who perceived lower levels of rigidity in their social environments felt significantly less lonely than those who perceived higher levels of social rigidity, though the association was weak in low income males. Thus, Japanese society and other high social rigidity cultures may need to reflect on the possibility that inflexible traditional norms of socialization are exacerbating loneliness.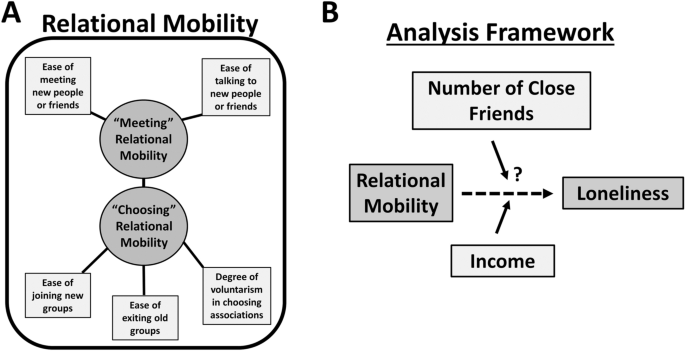
June 29, 2021
Subjective time compression induced by continuous action
Sayako Ueda and Shingo ShimodaAbstract
Increasing evidence indicates that voluntary actions can modulate the subjective time experience of its outcomes to optimize dynamic interaction with the external environment. In the present study, using a temporal reproduction task where participants reproduced the duration of an auditory stimulus to which they were previously exposed by performing different types of voluntary action, we examined how the subjective time experience of action outcomes changed with voluntary action types. Two experiments revealed that the subjective time experience of action outcomes was compressed, compared with physical time, if the action was performed continuously (Experiment 1), possibly enhancing the experience of controlling the action outcome, or if the action was added an extra task-unrelated continuous action (Experiment 2), possibly reflecting different underlying mechanisms from subjective time compression induced by the task-related continuous action. The majority of prior studies have focused on the subjective time experience of action outcomes when actions were performed voluntarily or not, and no previous study has examined the effects of differences in voluntary action types on the subjective time experience of action outcomes. These findings may be useful in situations in which people wish to intentionally compress their own time experience of daily events through their voluntary actions.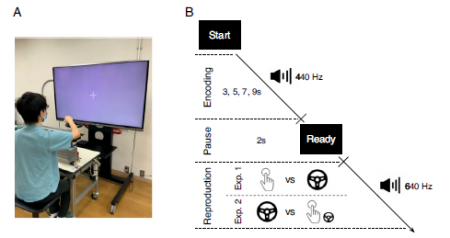
June 20, 2020
Multiscale Computation and Dynamic Attention in Biological and Artificial Intelligence
Ryan Paul Badman, Thomas Trenholm Hills & Rei AkaishiAbstract
Biological and artificial intelligence (AI) are often defined by their capacity to achieve a hierarchy of short-term and long-term goals that require incorporating information over time and space at both local and global scales. More advanced forms of this capacity involve the adaptive modulation of integration across scales, which resolve computational inefficiency and explore-exploit dilemmas at the same time. Research in neuroscience and AI have both made progress towards understanding architectures that achieve this. Insight into biological computations come from phenomena such as decision inertia, habit formation, information search, risky choices and foraging. Across these domains, the brain is equipped with mechanisms (such as the dorsal anterior cingulate and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex) that can represent and modulate across scales, both with top-down control processes and by local to global consolidation as information progresses from sensory to prefrontal areas. Paralleling these biological architectures, progress in AI is marked by innovations in dynamic multiscale modulation, moving from recurrent and convolutional neural networks—with fixed scalings—to attention, transformers, dynamic convolutions, and consciousness priors—which modulate scale to input and increase scale breadth. The use and development of these multiscale innovations in robotic agents, game AI, and natural language processing (NLP) are pushing the boundaries of AI achievements. By juxtaposing biological and artificial intelligence, the present work underscores the critical importance of multiscale processing to general intelligence, as well as highlighting innovations and differences between the future of biological and artificial intelligence. View Full-Text